
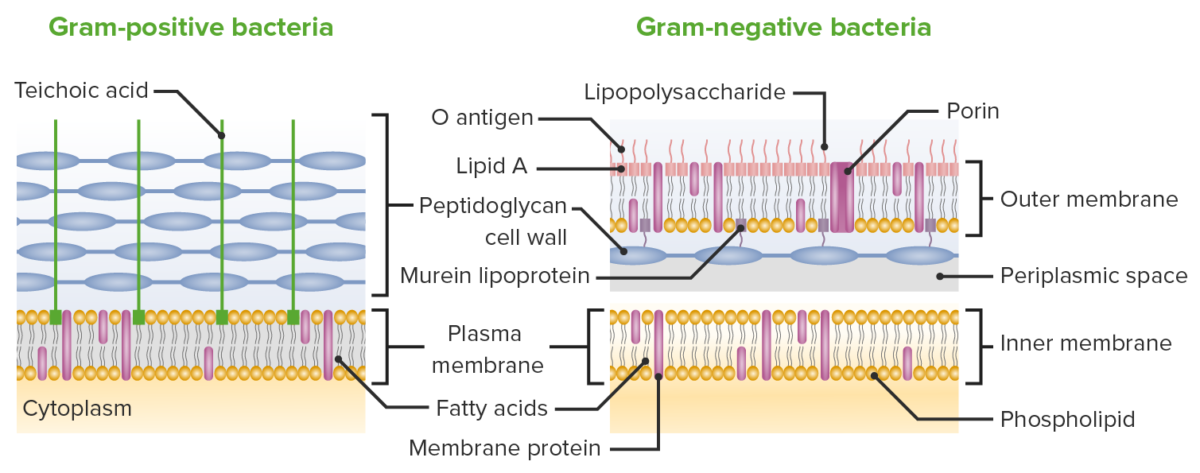
(left) Gram Stain of Staphylococcus aureus which are gram-positive (purple) cocci in clusters. Common Gram-positive bacteria of medical importance include Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Enterococcus faecalis, and Clostridium species. Gram-positive Bacteria: These retain the initial dye crystal violet during the Gram stain procedure and appear purple when observed through the microscope.Most bacteria can be placed into one of three groups based on their color after specific staining procedures are performed: Gram-positive, Gram-negative, or acid-fast. Gram-Positive, Gram-Negative, and Acid-Fast Bacteria You will learn more about the strategies antibiotics use to cross the cell wall in Week 3.\)). In contrast, the thick, porous peptidoglycan layer in the cell wall of Gram-positive bacteria gives greater access to antibiotics, allowing them to more easily penetrate the cell and/or interact with the peptidoglycan itself. This second, outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria is an effective barrier, regulating the passage of large molecules such as antibiotics into the cell. Figure 10 Arrangement of the cell wall in (a) Gram-positive and (b) Gram-negative bacteria. The inner membrane in (a) and (b) (shown as a double green line) is separated from the peptidoglycan layer by the periplasmic space. In the Gram-positive bacteria in (a) the peptidoglycan is a thick external layer shown in brown, while in the Gram-negative bacteria in (b) the peptidoglycan layer is much thinner and is surrounded by an outer membrane of lipopolysaccharide and protein (as a green wavy line). Gram-positive cell walls are structurally simple, containing a thick layer of peptidoglycan with embedded teichoic acid external to the plasma membrane.

There are two main categories of bacterial infections: Gram-positive and Gram-negative. Gram stains may also be used to check for bacteria in certain body fluids, such as blood or urine.
3 characteristics of gram negative bacteria cell wall skin#
(credit a: modification of work by Bibliomaniac. A Gram stain is a test that checks for bacteria at the site of a suspected infection such as the throat, lungs, genitals, or in skin wounds. cereus have been grown on sheep blood agar. (b) In this culture, white colonies of B. The small, pink cells are the gram-negative bacteria Escherichia coli.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/gram_negative_bacteria-5b7f308646e0fb002cbcdc5d.jpg)
The cell wall is metabolically inactive as it lacks. Figure 4.21 (a) In this gram-stained specimen, the violet rod-shaped cells forming chains are the gram-positive bacteria Bacillus cereus. The cell wall is thick, rigid, and has elastic properties that help them to grow in thickness over a period of time. There are two fundamental types of bacterial cell walls: Gram-positive cell walls, and Gram-negative cell walls. It is present in plant cells, fungi, bacteria and algae. Sequence the path of a solute from the external environment to the cytoplasm of a prokaryotic cell., Actually, there is much more to the cell wall than appears in Figure 4.6. The cell wall is the outermost and non-living part of the cell. This diagram shows the differences in cell wall structure between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Figure 3.26 Bacteria contain two common cell wall structural types. Difference Between Gram-Positive and Negative Cell Wall.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
